Cord Blood Basics
Why Store Cord Blood?
- Cord blood and cord tissue are rich in powerful stem cells that can only be collected at birth for potential future use.
- Stem cells can be used now for medical treatments. New therapies are being researched for potential future uses of cord blood and tissue, for conditions including type-1 diabetes, cerebral palsy and autism.
What is cord blood?
Cord blood is the blood that remains in your baby’s umbilical cord and placenta. Cord blood is a rich source of blood stem cells and other important cells.

Four benefits of cord blood banking
1. A perfect match for your baby
Should your baby ever need a stem cell transplant in the future, their own perfectly matched umbilical cord stem cells will be immediately available throughout their lifetime, with no risk of rejection.
Stem cells are matched based on human leucocyte antigen (HLA) markers, which act like signals to the body’s immune system. HLA matching is important since it improves the likelihood of a successful transplant. If the match is not perfect but still close, the odds are good that the recipient’s immune system will accept them. Because cord blood cells are less mature than bone marrow cells obtained from an adult, the matching criteria is less strict. An adult donor must match at least 6 of 8 HLA markers whereas a cord blood unit only needs to match 4 of 6 HLA markers.28
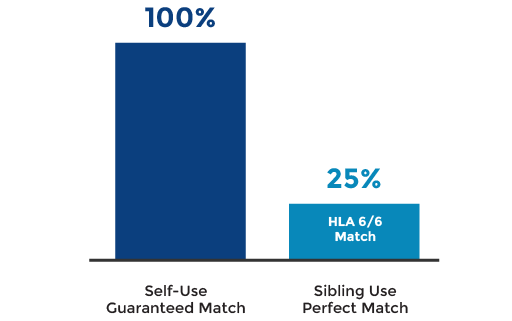
2. Potential match for your family
In the event that a stem cell transplant is required, problems of rejection will be eliminated by using a child’s own cells. Cord blood also has a greater potential to be a match for siblings compared to unrelated donors. Sibling cord blood has been associated with better clinical outcomes and fewer possible complications that may be associated with a third party donor.36
- There is a 25% chance that a sibling’s cord blood will be a perfect match.28
- Studies have shown that cord blood stem cells from a matched, related donor have less risk of rejection and a greater chance of acceptance than cells from an unrelated donor.5
- Other studies indicate that cord blood may not need to match as closely as is required for a marrow donor.28
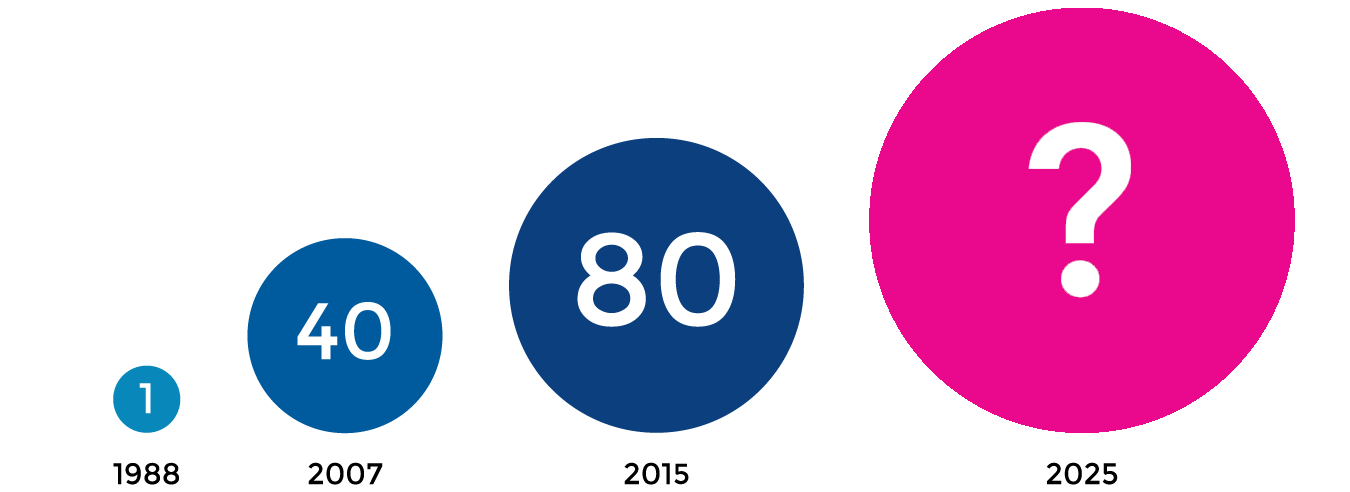
3. Used today in the treatment of over 80 diseases
Today, cord blood stem cells have been used in the treatment of over 80 life threatening diseases.37 There have been over 35,000 transplants38 worldwide using cord blood in place of bone marrow for conditions including:
- Solid tumors
- Cancers
- Genetic diseases
- Immune deficiencies
- Blood disorders and leukemias
So much has changed since the first cord blood transplant over 25 years ago. Today cord blood is used in the treatment of over 80 diseases! 10

4. Take advantage of emerging stem cell research
Scientific research is evaluating how cord blood cells may provide new therapies for a broad number of diseases for which there is no effective treatment today. While regenerative medicine has exciting potential, its prospects remain dependent on the success of ongoing research around the world.
If you think you have such a disease or have been at risk of exposure to such a disease, or if you are in doubt of your eligibility to participate, please call (1-866-606-2790 select option 2) and speak to one of our clinical consultants.
 Sign in
Sign in 

